
SEO Content Marketing Best Practices: Rank Higher & Drive Revenue
SEO content marketing represents the strategic intersection where valuable content meets search engine visibility. It’s not about gaming algorithms – it’s about creating content that serves real people while satisfying technical requirements. Google’s current priorities revolve around three core elements: helpful content that demonstrates genuine expertise, strong E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust), and solid Core Web Vitals performance.

The stakes are significant. According to recent data, the average #1 Google result captures 31.7% of clicks, while positions 2-10 combined get less than that. Meanwhile, organic search drives 53% of all website traffic – more than paid search and social combined. Companies investing in strategic SEO content marketing see an average ROI of 748%, far exceeding most digital marketing channels.
Yet most businesses fail at SEO content because they skip the foundational work. They publish without strategy, optimize without understanding intent, and wonder why traffic never materializes. This playbook changes that. You’ll learn the exact framework we use at NAV43 to help clients dominate search results while building genuine authority in their industries.
Phase 1: Audience & Keyword Intelligence
Every successful SEO content program begins with a deep understanding of the audience. You can’t rank for queries you don’t understand, and you can’t serve people whose needs remain mysterious. This phase transforms assumptions into data-driven insights that fuel your entire content engine.
Define Personas & Journey Stages
Start by mapping your audience’s actual behaviour, not demographics. What problems keep them searching at 2 AM? What questions do they ask colleagues? Document their journey from problem awareness through solution evaluation to decision-making. Each stage requires different content types and keywords.
For example, someone researching “marketing automation” (awareness stage) needs educational content about capabilities and benefits. But someone searching “HubSpot vs Marketo pricing” (decision stage) needs detailed comparisons and implementation guidance. Map these stages explicitly – they determine everything from keyword selection to content format.
Create 3-5 detailed personas focusing on goals, challenges, and search behaviour. Include their typical questions, preferred content formats, and trust signals they seek. This foundation ensures every piece of content serves a specific audience need rather than hoping for accidental relevance.
Intent-Driven Keyword Research
Keywords remain the foundation of SEO, but modern keyword research extends beyond volume metrics. Start with seed terms from your personas’ actual language – check support tickets, sales calls, and social media comments for authentic phrasing. Then expand using tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush, but filter everything through intent analysis.
Categorize keywords by search intent: informational (how/what/why questions), navigational (brand/product searches), commercial (reviews/comparisons), and transactional (buy/pricing/demo). Each intent type requires different content approaches. Informational keywords need comprehensive guides; transactional keywords need streamlined conversion paths.
Focus on long-tail keywords that reveal specific intent. “Content marketing” gets 165,000 monthly searches, but tells you nothing about user needs. “Content marketing strategy for B2B SaaS” gets 320 searches but revealsthe exact audience and intent. These specific queries often convert 2.5x better than head terms.
Don’t ignore zero-volume keywords either. Google’s algorithms understand semantic relationships – ranking for one specific query often captures hundreds of related searches. Plus, voice search and AI assistants generate unique long-tail queries that keyword tools miss entirely.
Competitive Gap Analysis
Your competitors’ content reveals market opportunities. Use tools like Ahrefs’ Content Gap feature to identify keywords where competitors rank but you don’t. More importantly, analyze their actual content quality. What questions do they leave unanswered? What expertise do they lack?
Create a competitive content matrix: list top competitors vertically, target topics horizontally, then grade each piece’s depth, accuracy, and user value. Look for patterns – perhaps everyone covers surface-level tips, but nobody shares implementation details. Those gaps become your opportunities.
Also, examine SERP features for target keywords. Featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and related searches reveal exactly what Google considers relevant. If every result includes video content or data visualizations, you’ll need those elements to compete effectively.
Phase 2: Strategy & Topic Clustering
Random blog posts don’t build authority – interconnected content ecosystems do. Topic clustering transforms isolated articles into comprehensive resources that dominate entire subject areas. This architectural approach signals expertise while creating multiple ranking opportunities.
Building Pillar Pages
Pillar pages serve as comprehensive guides to broad topics, typically 3,000-5,000 words covering every essential aspect. They’re not blog posts stretched thin – they’re authoritative resources that could stand alone as ebooks. Think “Ultimate Guide to Content Marketing” rather than “5 Content Tips.”
Structure pillar content with clear navigation, jump links, and logical flow from fundamentals through advanced concepts. Include original data, expert insights, and visual elements that make complex topics accessible. Each section should answer specific user questions while connecting to the broader theme.
For example, a pillar page on “Email Marketing Strategy” would cover list building, segmentation, automation, design, copywriting, analytics, and compliance – each section substantial enough to rank independently while contributing to the whole. This comprehensiveness signals topical authority to search engines.
Supporting Cluster Content
Cluster content delves into specific subtopics in detail, with each piece targeting long-tail keywords related to your pillar theme. These aren’t thin variations – each article provides unique value while reinforcing your site’s authority on the broader topic.
Plan 15-25 cluster pieces per pillar, covering different angles, use cases, and audience segments. A “Content Marketing” pillar might spawn clusters on topics such as “B2B content distribution,” “measuring content ROI,” “content brief templates,” and “repurposing blog content.” Each piece links back to the pillar and related clusters, creating a web of topical relevance.
This structure serves users navigating your content while sending strong topical signals to search engines. Sites using topic clusters experience an average organic traffic increase of 74% within six months, as the interconnected content reinforces expertise across related queries.
Editorial Calendar & Governance
Content consistency beats sporadic brilliance. Create an editorial calendar that maps content to business goals, seasonal trends, and audience needs. Include content types beyond blog posts – such as videos, tools, templates, and interactive content- to diversify your authority signals.
Establish governance standards covering voice, style, fact-checking, and update cycles. Document who approves content, how you verify claims, and when pieces get refreshed. This systematization ensures quality remains consistent as production scales.
Plan quarterly themes aligned with industry events or buyer cycles, but maintain flexibility for timely content. The best editorial calendars balance strategic planning with opportunistic agility – structure provides consistency while flexibility captures emerging opportunities.
Phase 3: Creating E-E-A-T Powered Content
Google’s E-E-A-T framework isn’t just another acronym – it’s the lens through which algorithms evaluate content quality. Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust determine whether your content ranks or languishes. Here’s how to demonstrate each element convincingly.

Showcasing Experience & Expertise
First-hand experience now weighs heavily in Google’s quality assessments. Generic advice compiled from other sources won’t cut it – you need authentic insights from actual implementation. Share specific examples, case studies, and lessons learned from real-world applications.
Author credentials matter more than ever. Create detailed author pages highlighting relevant education, certifications, professional experience, and published work. Link to LinkedIn profiles, industry associations, and previous authoritative content. For YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics, formal credentials become essential – financial advice needs certified professionals, health content requires medical expertise.
Include author bios on every piece, but go beyond generic descriptions. Explain why this specific author qualifies to address this topic. A cybersecurity article by someone with CISSP certification and 10 years defending Fortune 500 networks carries more weight than anonymous content. Schema markup for authors (Person schema) helps search engines recognize and validate expertise.
Authoritativeness & Trust Signals
Authority builds through consistent quality over time, but specific signals accelerate recognition. Citation quality matters more than quantity – link to primary sources, peer-reviewed research, and recognized industry authorities. When making claims, provide evidence. When sharing data, reveal sources and methodologies.
Trust signals extend beyond content to site-wide factors. Display clear ownership information, physical addresses, and legitimate contact methods. Industry certifications, association memberships, and security badges (SSL, privacy certifications) reinforce credibility. For e-commerce or service sites, reviews and testimonials provide social proof.
Transparency builds trust. Acknowledge content updates with revision dates. Disclose affiliations or potential conflicts. Correct errors publicly with editor’s notes. These practices demonstrate integrity while providing the accountability users and algorithms seek.
Content Depth, Formatting & Media
Comprehensive content consistently outranks superficial coverage, but depth means more than word count. Address topics thoroughly: cover fundamentals for beginners while including advanced insights for experts. Answer not just primary questions but anticipated follow-ups.
Format for both scanners and deep readers. Use descriptive headings that outline your content’s logic. Break up text with bullet points, numbered lists, and visual elements every 150-200 words. Pull quotes and callout boxes highlight key insights while tables and charts make data digestible.
Rich media serves both users and algorithms. Original images, custom graphics, and relevant videos increase engagement time while providing additional ranking opportunities. Every visual element needs optimization – compressed file sizes, descriptive filenames, and detailed alt text that serves accessibility while reinforcing topical relevance.
Phase 4: On-Page SEO Optimization Checklist
Technical optimization transforms good content into findable content. While user value matters most, proper implementation ensures search engines understand and surface your expertise. This checklist covers every critical element.
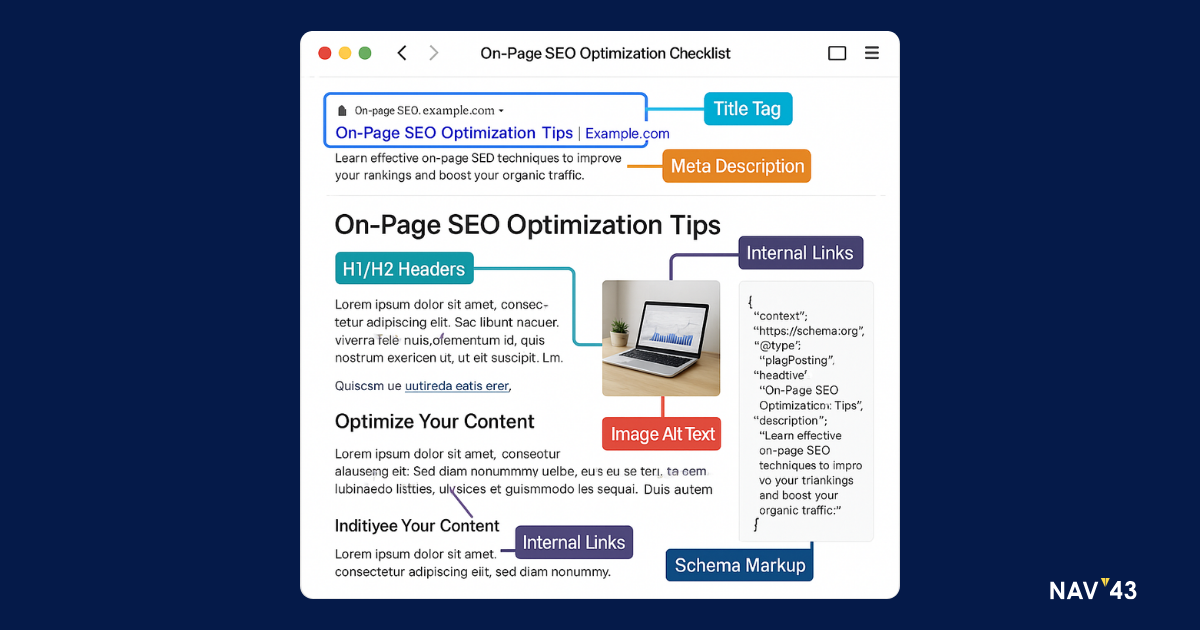
Title, Meta & URL Crafting
Title tags remain your most powerful on-page element. Front-load primary keywords within 60 characters while maintaining natural readability. “SEO Content Marketing: Complete 2024 Strategy Guide” beats “A Complete Guide to Content Marketing with SEO in 2024” because important terms appear first.
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings but influence click-through rates dramatically. Write compelling 150-160 character summaries that include keywords naturally while promising specific value. Test different approaches – questions, statistics, or benefit statements – to optimize CTR.
URLs should be clean, descriptive, and permanent. Use hyphens between words, exclude stop words (the, and, of), and keep them under 60 characters when possible. Once published, never change URLs without proper redirects – broken links destroy user experience and authority.
Header Hierarchy & Keyword Placement
Headers create content architecture that serves both users and crawlers. Use one H1 tag matching your title tag’s intent. Structure H2s as major sections, H3s as subsections, and H4s sparingly for detailed breakdowns. This hierarchy creates scannable content while reinforcing topical relevance.
Incorporate keywords naturally throughout headers, but prioritize clarity. “How to Research Keywords” beats “Keyword Research” as an H2 because it matches user language. Include semantic variations and related terms across subheadings to capture broader intent.
Within body content, mention primary keywords in the first 100 words, then naturally throughout. Focus on topic coverage rather than density – Google’s natural language processing recognizes comprehensive discussion without keyword repetition. Use bold text strategically to highlight important concepts, not to stuff keywords.
Multimedia & Structured Data
Images need strategic optimization beyond basic compression. Use descriptive filenames (seo-content-marketing-framework.jpg beats IMG_1234.jpg) and detailed alt text explaining what the image shows and why it’s relevant. Specify dimensions to prevent layout shift, improving Core Web Vitals scores.
Implement relevant schema markup to provide explicit context. Article schema clarifies content type, while FAQ or HowTo schemas can earn rich snippets. BreadcrumbList schema improves site navigation understanding. Test all markup using Google’s Rich Results Tool before publishing.
Don’t overlook technical performance. Lazy load images below the fold, serve next-gen formats (WebP), and use CDNs for faster delivery. Every millisecond of load time impacts user experience and ranking potential – pages loading in under 2.5 seconds have 24% lower bounce rates.
Phase 5: Promotion, Link Building & Distribution
Publishing great content represents half the battle – active promotion determines whether it reaches its audience. Strategic distribution and link building amplify authority signals while driving direct traffic that reinforces ranking potential.
Internal Linking Architecture
Internal links distribute authority while helping users and crawlers navigate your content ecosystem. Link cluster content to pillar pages using descriptive anchor text that reinforces topical relationships. Connect related posts within clusters to strengthen semantic connections.
Avoid generic anchors like “click here” or “read more.” Instead, use descriptive phrases that preview the linked content’s value. “Learn how to map customer journey stages” beats “see our customer journey guide” because it provides context while including relevant terms.
Audit internal linking quarterly to fix broken connections and identify orphaned content. Pages without internal links struggle to rank regardless of quality. Tools like Screaming Frog reveal linking gaps while visualizing site architecture opportunities.
Earning Backlinks & Digital PR
Quality backlinks remain crucial ranking factors, but link building evolved from volume games to relationship building. Create link-worthy assets: original research, interactive tools, comprehensive guides, or controversial perspectives backed by data. Content that provides unique value naturally attracts citations.
Develop digital PR strategies targeting industry publications, relevant blogs, and journalist queries (HARO). Pitch specific angles rather than generic content. A data study on “B2B content marketing budgets” interests trade publications more than another “content marketing tips” post.
Build relationships before requesting links. Share others’ content, provide expert commentary, and offer genuine value to their audiences. When you do request links, explain specifically how your content helps their readers. This approach yields higher-quality links than mass outreach.
Amplification Channels (Social, Email)
Social amplification drives initial traffic surges that signal content value to search engines. But platform-specific optimization matters – what works on LinkedIn fails on Twitter. Craft platform-native posts highlighting different content angles for each audience.
Email remains your most controllable distribution channel. Segment lists by interest and engagement level, personalizing content recommendations. Include social sharing buttons and encourage forwarding to expand organic reach. Email-driven traffic typically shows higher engagement metrics, reinforcing quality signals.
Repurpose content across formats to maximize reach. Transform blog posts into video scripts, infographics, podcast episodes, or email courses. Each format reaches different audience segments while creating additional ranking opportunities across platforms.
Phase 6: Measurement, Iteration & Content Refresh
Publishing isn’t the finish line – it’s where optimization begins. Systematic measurement and iteration separate high-performing content programs from those hoping for accidental success.
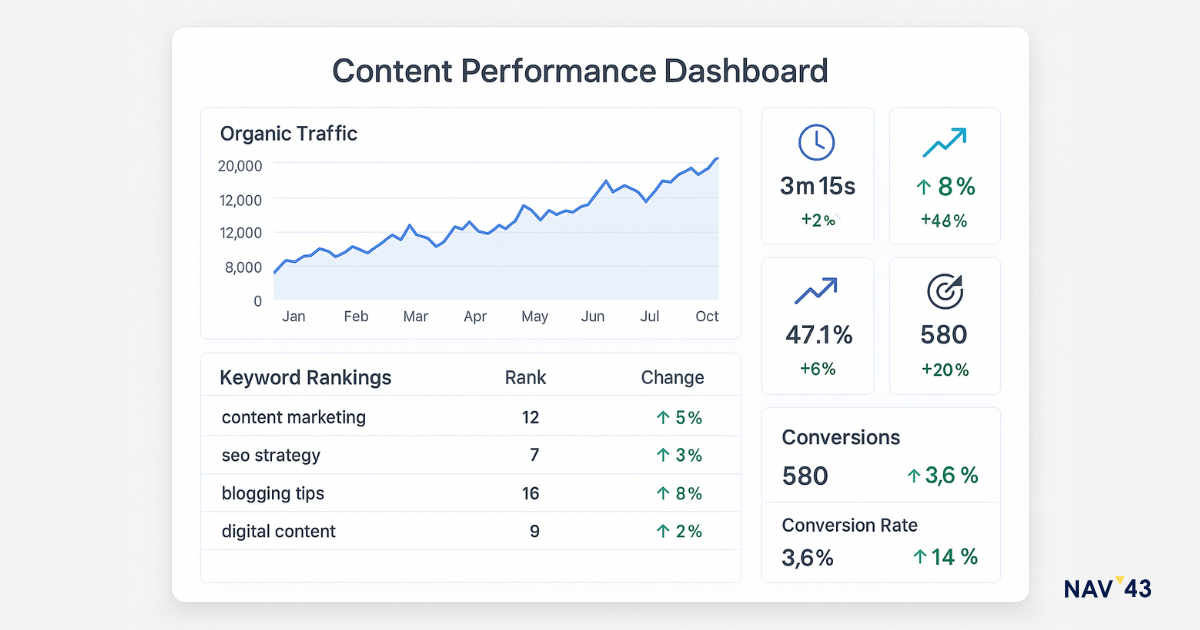
Core KPIs & Reporting
Track metrics that matter for business impact, not vanity statistics. Organic traffic growth, keyword rankings, and backlinks indicate SEO success, but conversion rates, qualified leads, and revenue attribution prove ROI. Build dashboards connecting content performance to business outcomes.
Monitor user engagement through average session duration, pages per session, and scroll depth. Low engagement signals content-user mismatch regardless of rankings. Google’s algorithms increasingly factor user satisfaction signals – high bounce rates and quick returns to search results indicate poor content quality.
Use Search Console to identify optimization opportunities. Click-through rates below 2% suggest title/meta improvements needed. Queries generating impressions, but few clicks reveal content gaps. Pages losing rankings need refresh priority.
Update Cadence & Optimization Loops
Content freshness impacts rankings significantly for time-sensitive topics. Establish update cycles based on content types: news-related content needs monthly reviews, evergreen guides quarterly updates, and pillar pages semi-annual overhauls. Document changes to track what drives performance improvements.
Don’t just update dates – add substantial value. Include new data, additional examples, emerging trends, or improved explanations. Google’s freshness algorithms detect cosmetic changes versus meaningful updates. Pages with 20%+ new content typically see ranking improvements within weeks.
A/B test systematically to optimize conversions. Test headlines, meta descriptions, CTA placement, and content structure. Small improvements compound – increasing CTR from 2% to 3% means 50% more traffic from the same rankings.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Most SEO content failures stem from predictable mistakes. Here are the most damaging pitfalls and their solutions:
Keyword stuffing: Forcing keywords unnaturally destroys readability and triggers penalties. Instead, focus on comprehensive topic coverage using natural language variations.
Thin content: Publishing numerous shallow pieces dilutes authority. Consolidate similar topics into comprehensive resources that thoroughly address user intent.
Ignoring user experience: Optimizing for bots while frustrating humans guarantees failure. Prioritize fast load times, mobile optimization, and intuitive navigation.
Neglecting E-E-A-T: Anonymous, unsourced content can’t compete. Invest in demonstrating genuine expertise through author credentials and authoritative citations.
Set-and-forget mentality: Abandoned content decays rapidly. Schedule regular audits and updates to maintain rankings.
Isolated content creation: Disconnected posts waste potential. Build topic clusters that reinforce authority through strategic internal linking.
Conclusion & Next Steps
SEO content marketing success requires systematic execution across six phases: audience intelligence, strategic planning, E-E-A-T content creation, technical optimization, active promotion, and continuous improvement. Skip any phase and results suffer.
The payoff justifies the effort. Clients following this playbook see average organic traffic increases of 200% within 12 months, with some achieving 10x growth in competitive markets. More importantly, they build sustainable competitive advantages through genuine topical authority.
Start with one topic cluster. Choose a subject central to your business, conduct thorough research, and create genuinely helpful content that demonstrates expertise. Optimize technically, promote strategically, and iterate based on data. Success in one cluster provides the template for dominating your entire market.
Stop guessing at SEO content success. Get the exact framework we use to help clients dominate search results while building lasting authority. Download your checklist now and start ranking for the queries that matter.
