
Every LinkedIn Ads Targeting Option Explained (With Real-World Use-Cases
If you’re running B2B campaigns, LinkedIn’s recent targeting overhaul for ads management might have you scratching your head. They’ve sunset Lookalikes and rolled out Predictive Audiences, leaving many marketers wondering which levers to pull for optimal audience targeting and results.
The difference between precision and waste often comes down to understanding which targeting combinations work for specific business objectives. According to LinkedIn’s own data, campaigns with well-optimized targeting see up to 30% higher conversion rates than those using broader approaches.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know every dial you can turn, when to turn it, and get a swipe file of targeting recipes that have consistently delivered results for our clients.
The Targeting Framework at a Glance
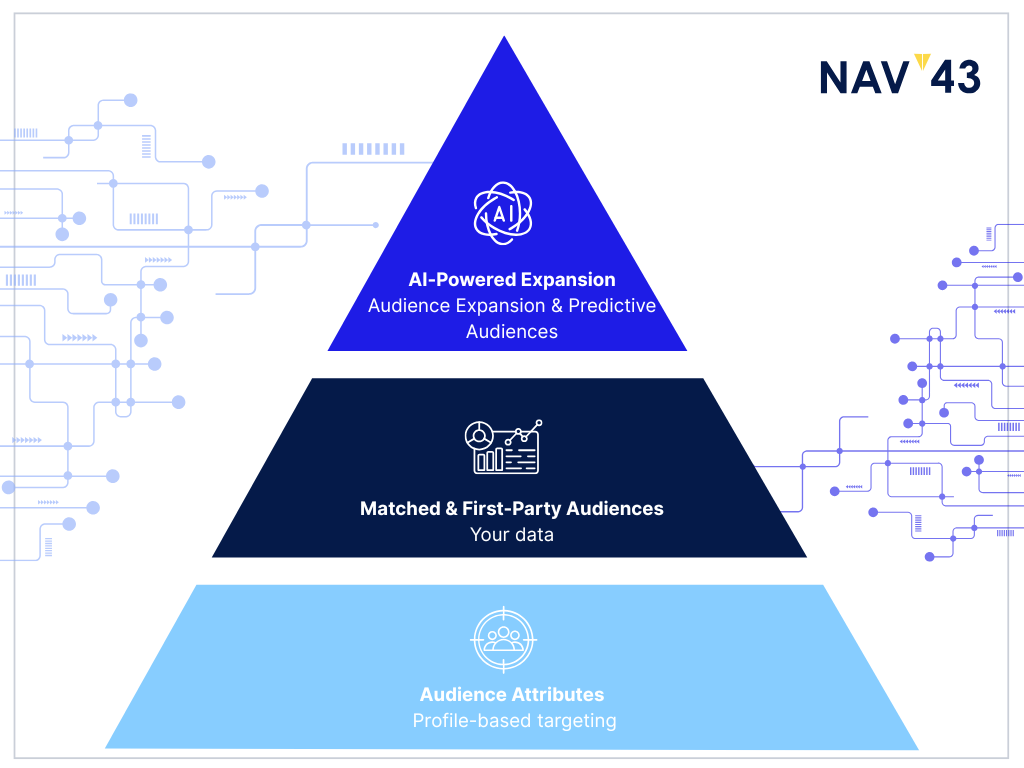
LinkedIn’s targeting ecosystem rests on three core pillars:
- Audience Attributes (profile-based targeting)
- Matched & First-Party Audiences (your data)
- AI-Powered Expansion Layers (Audience Expansion & Predictive Audiences)
These work together to create a comprehensive targeting approach that can be fine-tuned for virtually any B2B campaign objective, from targeted ABM initiatives to broader awareness plays. Understanding these pillars and following best practices can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your LinkedIn ad campaigns.
Audience Attributes: Profile-Based Targeting Options
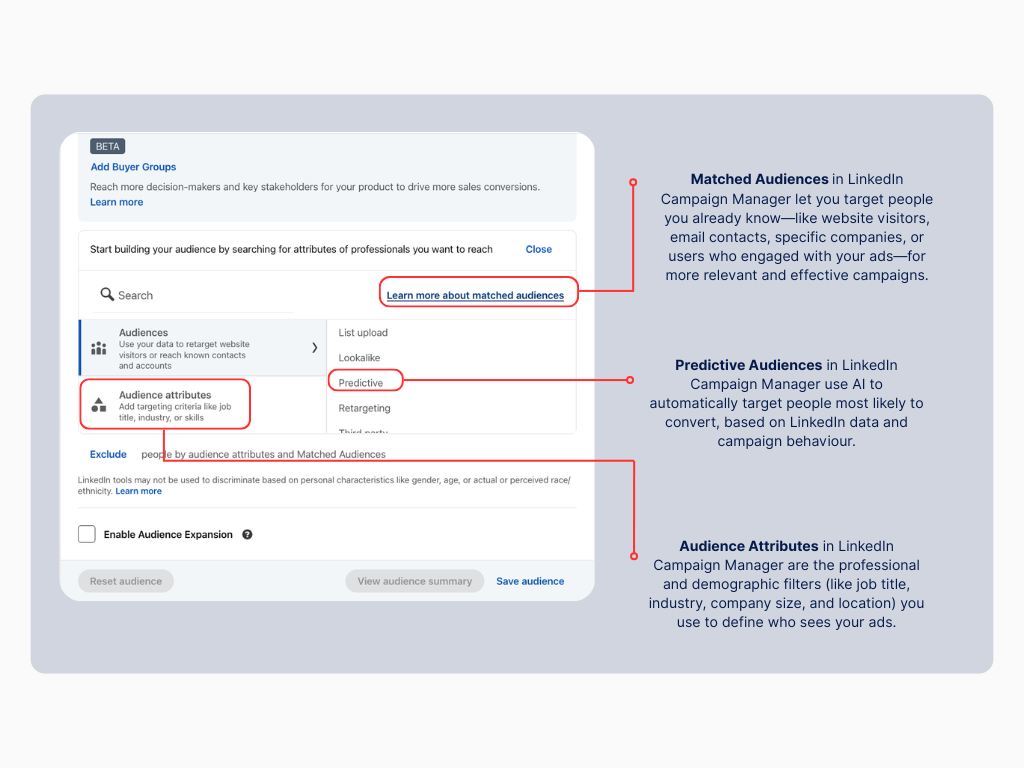
LinkedIn’s profile-based targeting options leverage the professional information users voluntarily share on their profiles. Let’s break down each attribute and how to use them effectively.
Additionally, targeting based on member skills can help you reach individuals with specific expertise relevant to your campaign.
Location Targeting
Definition: Targets members based on their profile location and recent activity signals. This includes targeting based on recent location data, which can be particularly useful for businesses aiming to engage potential clients who have recently visited specific cities or regions.
Minimum Audience Size: Required for all campaigns
Use Case: When planning a cross-border SaaS roadshow, targeting specific cities like Toronto and Boston simultaneously with location-specific messaging and event details typically yields higher registration rates compared to generic geographic approaches.
Language
Definition: Filters members based on their chosen LinkedIn interface language.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: For multilingual markets like Canada, serving French creative to Quebec prospects while maintaining English messaging elsewhere can improve engagement rates substantially, according to LinkedIn’s internal case studies.
Company Targeting
Definition: Leverages data from 63 million company pages to filter by size, industry, name, and growth signals. This includes targeting by company industry, which allows advertisers to reach decision-makers within specific sectors.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: For enterprise SaaS campaigns, targeted ABM approaches to Fortune 100 FinTech companies create opportunities for hyper-relevant messaging that addresses specific industry pain points.
Job Experience
Definition: Filters based on parsed job history, including title, function, seniority, and years of experience. This includes targeting by job seniority, which helps in reaching users within a company’s hierarchy based on their rank or level of influence.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: When promoting advanced analytics tools, targeting “VP Growth” and “Director of Analytics” roles with at least 10 years of experience ensures reaching decision-makers with budget authority.
Education
Definition: Targets based on degree type, field of study, and school.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: For professional development programs, we target STEM master’s graduates who are likely seeking to enhance their technical qualifications.
Demographics
Definition: Includes age and gender as reported or inferred by LinkedIn. This includes targeting by member age and member gender, which are crucial demographic options for audience segmentation.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: Primarily used for audience research rather than optimization. Demographic breakdowns help refine understanding of who responds to specific messaging types.
Interests & Traits
Definition: Groups members based on content engagement and activity patterns. This includes targeting based on product interests, which can help in reaching specific decision-makers within established groups.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: For AI tool promotions, targeting the “Artificial Intelligence” interest cluster has consistently outperformed broader technology targeting, according to LinkedIn’s 2024 Benchmark Report.
Groups
Definition: Targets members of specific LinkedIn Groups.
Minimum Audience Size: 300 members
Use Case: For revenue operations tools, sending Message Ads to members of “RevOps & RevGenius” groups typically yields higher conversion rates versus standard job function targeting, according to case studies presented at LinkedIn Marketing Labs.
Matched & First-Party Audiences: Leverage Your Data
First-party data often represents your most valuable targeting asset. LinkedIn offers several ways to activate this data. Effective audience creation is crucial for leveraging first-party data to its fullest potential.
Website Retargeting
Definition: Pixel-based audience building that segments visitors by URL patterns and timeframes, ensuring you reach users who are already engaged with your content.
Best For: Mid-funnel nurturing campaigns
Example: SaaS companies often show case study videos to pricing page visitors, which Social Media Examiner reports can increase demo requests by up to 40% compared to cold targeting.
Engagement Retargeting
Definition: Captures users who’ve interacted with your content through video views, Lead Gen Form opens, or ad clicks, allowing you to re-engage them effectively.
Best For: Warm audience nurturing
Example: LinkedIn’s own marketing team found that users who watched more than 75% of product demo videos and then received follow-up ads with customer testimonials converted at a significantly higher rate.
Contact List Uploads
Definition: Target existing contacts by uploading CSV files or syncing with HubSpot.
Best For: Account-based marketing and customer upsells
Example: HubSpot’s case studies show that segmenting existing users to promote premium features often results in 3x higher ROI on ad spend compared to cold acquisition campaigns. This method can be particularly effective when combined with company lists to refine your audience further.
Company List Uploads
Definition: Target specific organizations by uploading company names or domains.
Best For: Account-based marketing at scale
Example: According to DemandGen Report, enterprise software companies targeting their top prospect companies with tailored messaging achieve significantly higher engagement than using industry targeting alone.
Additionally, targeting company connections can help optimize B2B marketing efforts by narrowing down the audience to relevant decision-makers.
CRM Segments via Conversions API
Definition: Dynamically push segments from your CRM based on lifecycle stage or behavior.
Best For: Pipeline acceleration
Example: Leading CRM providers report that targeting “opportunity” stage prospects with ROI calculators can contribute to shorter sales cycles for enterprise deals.
Predictive Audiences (2025)
Definition: AI-powered audience expansion that builds propensity models from seed lists.
Best For: Finding net-new prospects similar to your best customers
Example: Early adopters in the LinkedIn Marketing Partner program report that using seed lists of enterprise customers who converted quickly can create Predictive Audiences that deliver similar-quality leads at competitive acquisition costs. This method helps in identifying your ideal audience by leveraging AI-powered models.
AI & Expansion Layers: Scale With Intelligence
LinkedIn has invested heavily in AI-powered targeting features to help advertisers expand reach while maintaining relevance.
These features allow for audience-based targeting, ensuring that your ads reach the most relevant users.
Audience Expansion
Definition: Automatically includes members “similar” to your selected targeting attributes.
When to Use: Enable for awareness campaigns and disable for precise ABM initiatives.
Pro Tip: Marketing experts find that enabling Audience Expansion works best when you’ve already built a highly targeted core audience that might be too small for sufficient delivery. This approach helps in reaching different audiences that share similar attributes to your core target group.
Predictive Audiences vs. Old Lookalikes
Predictive Audiences represents a significant upgrade over the deprecated Lookalike Audiences:
| Feature | Predictive (2025) | Lookalike (legacy) |
| Source data | AI model using seed list + on-platform engagement | Seed list demographics only |
| Size control | Manual percentage slider | Fixed at 1× seed size |
| Performance monitoring | Detailed breakdown reporting | Limited visibility |
| Availability | All B2B campaign objectives | Deprecated February 2024 |
Key Insight: According to DXI’s LinkedIn Ads Benchmark Report, Predictive Audiences have delivered up to 30% higher quality leads (measured by sales qualification rate) compared to the old Lookalike Audiences, while maintaining similar CPLs. Understanding the target audience size is crucial for optimizing the performance of Predictive Audiences.
Combining Options: Boolean Logic 101
Mastering LinkedIn targeting means understanding how to combine options effectively:
This target-based approach ensures that your campaigns reach the appropriate audience for better engagement and efficiency.
AND Logic (Narrows Audience)
Combining attributes with AND logic creates a more precise audience where members must match all conditions.
Example: Targeting Technology Industry AND Director-level Seniority AND Marketing Function creates a highly qualified but smaller audience. This ensures that your ads are seen by the right people who are most likely to engage with your content.
OR Logic (Expands Audience)
Using OR logic between similar attributes creates a broader pool while maintaining relevance.
Example: Targeting “CMO” OR “VP Marketing” OR “Head of Marketing” job titles captures the same decision-maker level across different organizational structures.
This approach helps in reaching different audiences that share similar attributes to your core target group.
EXCLUDE Logic (Refines Audience)
Strategic exclusions can improve campaign efficiency:
- Exclude competitors to prevent wasted impressions
- Exclude employees unless running internal campaigns
- Exclude previous converters for acquisition campaigns
For example, excluding competitors based on company name can prevent wasted impressions.
Pro Tip: When working with multiple audiences, use the audience preview tool to estimate potential overlap and adjust accordingly.
“Targeting Recipes” Gallery
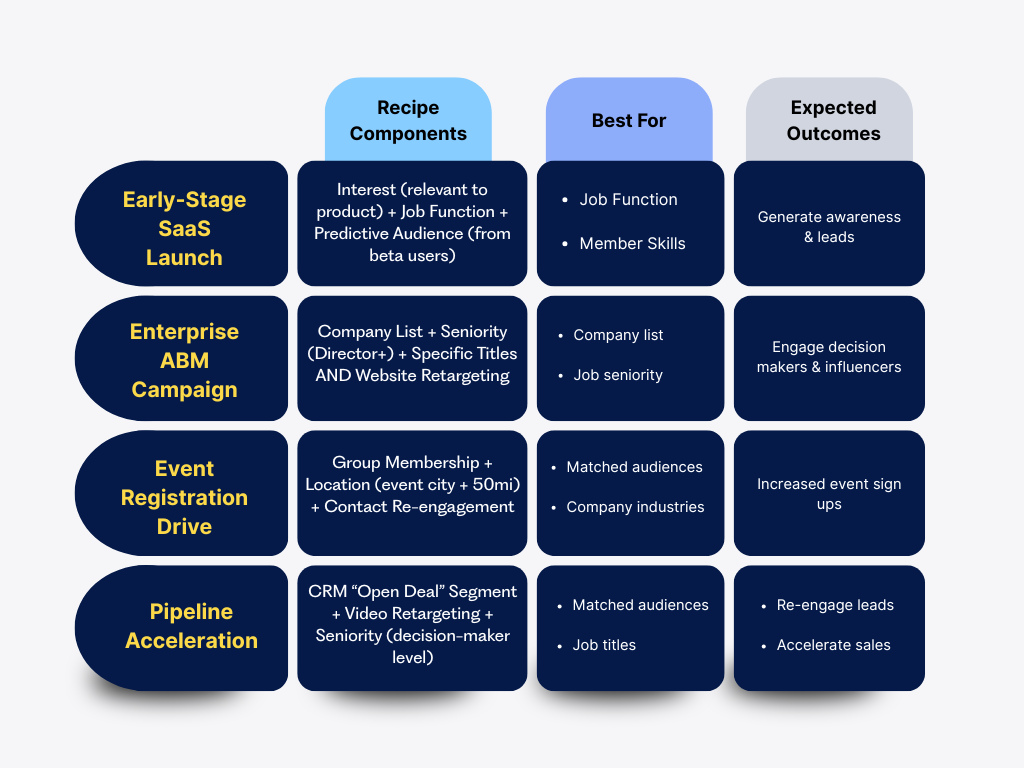
These proven combinations deliver consistent results for specific campaign objectives:
Each ad campaign should be tailored to specific objectives to ensure optimal results.
Early-Stage SaaS Launch
Recipe: Interest (relevant to product) + Job Function + Predictive Audience (from beta users)
Why It Works: This combination balances interest-based targeting with functional relevance, then scales through AI-driven expansion. This approach effectively engages users at various stages of their buying journey.
Success Story: LinkedIn’s Advertising Solutions team documented a case where a marketing automation company used this approach and achieved CTRs well above the platform benchmark, generating significant qualified leads in their launch month.
Enterprise ABM Campaign
Recipe: Company List + Seniority (Director+) + Specific Titles AND Website Retargeting
Why It Works: Creates a precise target at key accounts while capturing both cold prospects and those already showing interest.
Success Story: According to case studies presented at B2B Marketing Exchange, this approach has helped enterprise software companies generate qualified opportunities at target accounts within a single quarter, with a significant portion of conversions coming from the retargeting segment. Leveraging your company page can enhance the effectiveness of this approach by promoting tailored content to key accounts.
Event Registration Drive
Recipe: Group Membership + Location (event city + 50mi) + Contact Re-engagement
Why It Works: Combines location relevance with demonstrated interest and past engagement. Focusing on the permanent location of potential attendees can further enhance the effectiveness of this approach.
Success Story: Event marketing platform Bizzabo reported that tech conferences using this targeting approach consistently fill a higher percentage of available seats at a lower cost-per-registration compared to broader targeting methods.
Pipeline Acceleration
Recipe: CRM “Open Deal” Segment + Video Retargeting + Seniority (decision-maker level)
Why It Works: Focuses resources on prospects actively in the sales process while ensuring content reaches decision-makers. This approach ensures that your campaigns are aligned with the customer journey, enhancing the likelihood of conversion.
Success Story: Forrester’s research on B2B buying cycles indicates that targeted LinkedIn campaigns can contribute to reduced sales cycle lengths for enterprise deals, with significant influence on pipeline acceleration.
Measurement & Optimization
Beyond setup, ongoing optimization is crucial for LinkedIn campaign success:
Implementing these practices can significantly improve the performance of your LinkedIn ad campaigns.
Performance Monitoring
Break out performance metrics by attribute in Campaign Manager to identify which segments are driving results.
Benchmark: Aim for CTR ≥ 0.55% for layered audiences. If you’re seeing < 0.4%, consider revising your targeting or creative approach.
Analyzing how users interact with your content on LinkedIn can provide valuable insights for optimizing your campaigns.
Creative Rotation
Fatigue hits faster in professional networks. Rotate creative assets every 2-3 weeks to maintain Relevance Score.
Pro Tip: LinkedIn’s own research shows performance improvements of up to 35% by implementing systematic creative rotation calendars for long-running campaigns.
Refreshing your ad copy regularly can help maintain audience engagement and improve performance.
Budget Allocation
Allocate at least 70% of budget to your proven targeting combinations, but reserve 30% for testing new approaches. Allocating a portion of your budget to sponsored content campaigns can help extend your reach and enhance engagement.
Putting It All Together
LinkedIn’s targeting ecosystem offers over 20 different dials to turn, but success doesn’t come from using all of them simultaneously. Strategic combinations aligned with specific campaign objectives consistently outperform scattered approaches.
According to LinkedIn’s own research, the most successful advertisers start with a clear understanding of their ideal customer profile, translate that into a targeted combination of attributes, and then use data to refine and optimize over time.
Ready to take your LinkedIn targeting to the next level? Book a targeting strategy call with our team to discuss your specific needs. By mastering LinkedIn advertising, you can significantly enhance your marketing efforts and achieve your business objectives.
-
LinkedIn deprecated Lookalike Audiences in February 2024. Use Predictive Audiences instead for similar functionality with improved performance.
-
Aim for at least 300 members for Matched Audiences and a minimum of 50,000 for Predictive Audience seed lists to ensure sufficient reach.
-
Yes, members may overlap between your core targeting and expansion. Check the Breakdown › Delivery report to understand the contribution of each segment.
-
Upload your company domain as a list in the Exclusions section of your campaign setup.
-
Not currently. Predictive Audiences replace all other attribute targeting when selected. Generally speaking, understanding the nuances of LinkedIn's targeting options can help you troubleshoot common issues more effectively.
