
How Often Should You Do A Technical SEO Audit? The 2025 Guide
Introduction to SEO Audits
An SEO audit is the digital equivalent of a comprehensive health check-up for your website, evaluating its performance from an SEO perspective to ensure it’s optimized for search engines. Think of it as a diagnostic process that uncovers hidden issues affecting your site’s ability to rank and attract organic traffic. Regular SEO audits are essential for maintaining strong search engine visibility and supporting your broader digital marketing goals.
Technical SEO audits dive deep into the back-end elements of your site—things like site speed, mobile friendliness, and broken links—that aren’t visible to users but are critical for search engine performance. By systematically identifying issues such as slow-loading pages, poor mobile experiences, or technical errors, you can address problems before they impact your rankings or user experience. In today’s competitive online landscape, regular SEO audits are not just a best practice—they’re a necessity for any business serious about digital marketing and sustained search engine success.
Why Ongoing SEO Audits Aren’t One-and-Done
Let’s get one thing straight: treating your SEO audit like a yearly dentist visit you can skip is a recipe for ranking decay. Google makes over 5,000 algorithm updates annually, that’s roughly 14 changes every single day. While most are minor, the cumulative effect of ignoring these shifts is like compound interest working against you.
Think about what happens to an unaudited site over 12 months. Broken links multiply like digital weeds. Orphan pages pile up from content updates and deletions. Your Core Web Vitals slowly degrade as new scripts and images bloat page weight. Meanwhile, competitors who audit quarterly are fixing these issues before they compound. For highly competitive sites, monthly SEO audits are often necessary to catch and resolve issues before they impact rankings.
The technical debt accumulation is real. I recently audited a site that hadn’t been checked in two years. The damage? 347 broken internal links, 89 orphaned pages, and mobile page speeds averaging 4.2 seconds. Their organic traffic had declined 42% year-over-year, not from any penalty, but from death by a thousand technical cuts. In depth audits are essential to uncover hidden or compounding issues that standard checks might miss.
Beyond the technical decay, competitive dynamics shift constantly. Your rivals aren’t standing still. They’re optimizing, testing, launching new content strategies. When you audit annually while they audit quarterly, you’re essentially giving them three extra optimization cycles to outmaneuver you. In competitive verticals like SaaS or e-commerce, that gap can mean the difference between page one and page three. Comprehensive SEO audits every few months are critical to maintain visibility and adapt to ongoing changes.
The reality is that SEO maintenance is continuous optimization, not periodic housekeeping. Your site exists in a dynamic ecosystem where search algorithms evolve, user behavior shifts, and technical standards advance. Treating audits as one-and-done is like assuming your business strategy from 2022 still works perfectly in 2025. It doesn’t, and neither does your SEO. After major site updates or notable performance drops, conducting a major SEO audit is crucial to ensure your site’s health and alignment with current SEO standards.
Benefits of Regular Audits
Conducting regular SEO audits delivers a host of benefits that go far beyond just ticking a box. First and foremost, they help boost your search engine rankings by ensuring your site is easily crawlable and indexable by search engine bots. By catching and fixing technical SEO issues early—whether it’s a misconfigured robots.txt, slow-loading pages, or broken internal links—you make it easier for search engines to discover and rank your content.
Regular audits also help you stay ahead of the curve as search engine algorithms evolve. With Google and other search engines constantly updating their ranking factors, quarterly SEO audits can help you adapt quickly, preventing sudden drops in search engine rankings. Monthly audits, meanwhile, provide valuable insights into your site’s ongoing performance, allowing you to make data-driven decisions and continuously improve your SEO strategy. Ultimately, regular SEO audits are your best defense against technical decay, helping you maintain a healthy, high-performing website that delivers results.
Audit Frequency Benchmarks at a Glance
Not every site needs the same audit cadence. Your ideal frequency depends on site complexity, update velocity, competitive pressure, and your website’s size. Larger or more complex sites may require more frequent audits to proactively address potential issues. Here’s what actually works in practice:
Small Brochure Sites (Annual Audits)
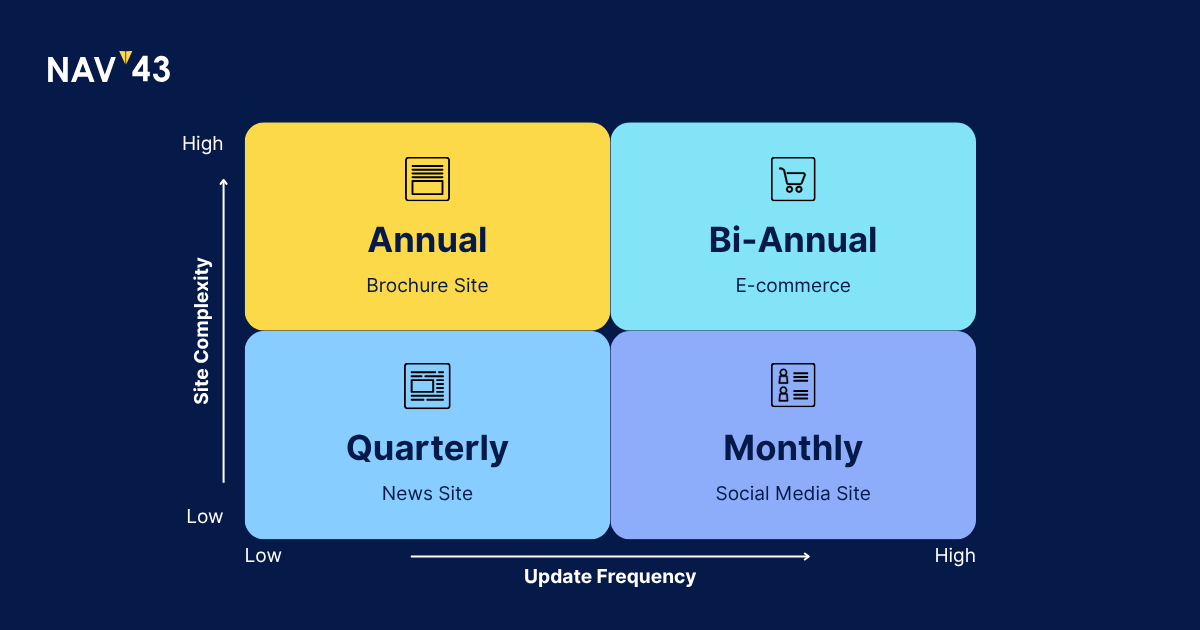
If you’re running a 10-50 web page local business site that rarely changes, an annual SEO audit suffices. These sites accumulate issues slowly, maybe some broken links, outdated meta descriptions, or shifting local search factors. A yearly deep dive catches these problems before they impact visibility. Schedule it like an annual physical: same month every year, comprehensive review, action plan for the year ahead.
Growing SMB / Content Hubs (Semi-Annual Audits)
Sites publishing regular content or managing 100-500 web pages need audits every six months. Why? Content velocity creates more failure points. New pages can cannibalize existing rankings. Internal linking structures degrade. Technical issues multiply faster. These sites benefit from a January and July audit rhythm, catching post-holiday technical debt and mid-year course corrections.
Large E-commerce & Publishers (Quarterly Audits)
Once you’re managing thousands of web pages, quarterly audits become essential. E-commerce sites face constant flux: products launching and retiring, category restructuring, promotional landing pages. Publishers deal with content pruning, topic clustering evolution, and Core Web Vitals at scale. Quarterly audits align with business quarters, making it easier to tie SEO improvements to revenue impact. For large content operations, fixing orphan pages by adding an internal link is crucial for improving discoverability and indexing.
News Sites & Hyper-Competitive Niches (Monthly Checks + Quarterly Deep Dives)
If you’re in news, finance, or cutthroat e-commerce verticals, monthly spot checks supplemented by quarterly comprehensive audits keep you competitive. The monthly checks focus on critical metrics: indexation rates, crawl budget efficiency, breaking technical issues. The quarterly deep dives handle strategic elements like competitor gap analysis and content optimization opportunities.
Here’s the framework distilled:
- Annual: Static sites, minimal updates, low competition
- Bi-Annual: Regular content publishing, moderate competition
- Quarterly: High-volume sites, aggressive competition, frequent changes
- Monthly: News/trending content, extreme competition, real-time optimization needs
For effective audits, especially on larger or more complex sites, combine manual and automated checks. Regular automated audits help with frequent monitoring, while manual checks provide in-depth reviews to catch issues automated tools might miss.
Choosing the Right Cadence for Your Site
Generic audit schedules fail because they ignore your specific situation. Let’s build a custom cadence using four critical factors that determine your ideal audit frequency.
Site Complexity Multipliers
Page count alone doesn’t determine complexity. A 500-page site with five templates is simpler than a 200-page site with custom layouts everywhere. Consider these complexity factors:
- Template diversity: More templates mean more potential breaking points
- Multi-language versions: Each language multiplies your audit surface area
- Dynamic content: User-generated content, real-time inventory, personalization
- Technical stack: JavaScript frameworks, third-party integrations, CDN configurations
Regular technical SEO audits are essential to maintain your site’s performance, as they help identify and resolve issues like broken links, redirect loops, and incorrect canonicals that can negatively impact both rankings and user experience.
Rule of thumb: Each complexity multiplier should increase your audit frequency by one level. Running a multi-language e-commerce site with dynamic pricing? That’s quarterly minimum, possibly monthly.
Update Velocity Assessment
How often does your site change? Track these metrics over three months:
- New pages published per month
- Existing pages modified per month
- Product/service launches
- CMS or platform updates
- Design refreshes or A/B tests
If you’re changing more than 10% of your site quarterly, you need quarterly audits. Anything above 25% quarterly change demands monthly spot checks to catch issues early.
Industry Volatility Factors
Some industries face constant SERP upheaval. I analyzed SERP volatility across industries and found massive variance. Your Money Your Life (YMYL) sectors see 3x more ranking fluctuation than B2B manufacturing. High-volatility industries include:
- Healthcare and medical
- Financial services
- Legal services
- News and media
- Trending e-commerce (fashion, electronics)
In volatile industries, your audit frequency should match your competitors’ optimization velocity. If top competitors update content weekly, your quarterly audit schedule leaves you perpetually behind.
Resource Reality Check
Perfect audit schedules mean nothing without execution capacity. Be realistic about:
- Team bandwidth: Who actually implements audit recommendations?
- Technical resources: Can developers prioritize SEO fixes?
- Budget allocation: Tools, consultants, implementation costs
- Risk tolerance: What’s the cost of ranking drops versus audit investment?
Better to execute quarterly audits thoroughly than attempt monthly audits that generate ignored recommendations. Match frequency to your implementation capacity.
To ensure your ongoing SEO practices are effective, include frequent audits as part of your regular optimization efforts. Based on the factors above, audit your site at a cadence that matches your complexity, update velocity, industry volatility, and available resources.
Pre-Audit Preparation
Before diving into an SEO audit, preparation is key to ensuring your efforts are focused and effective. Start by clearly defining your objectives—are you looking to improve technical SEO health, boost on-page SEO, or address a recent drop in rankings? Next, determine the scope of your audit: will you review the entire site or focus on specific sections?
Gather essential tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to collect the data you’ll need for a thorough SEO audit. Consider your website’s size, complexity, and the competitiveness of your industry when planning your audit schedule. For example, a highly competitive industry may require more frequent audits to stay ahead, while a local business might prioritize local SEO audits. By tailoring your approach and assembling the right resources, you’ll set the stage for a successful and thorough SEO audit that delivers actionable insights.
Trigger Events That Demand Immediate SEO Audits
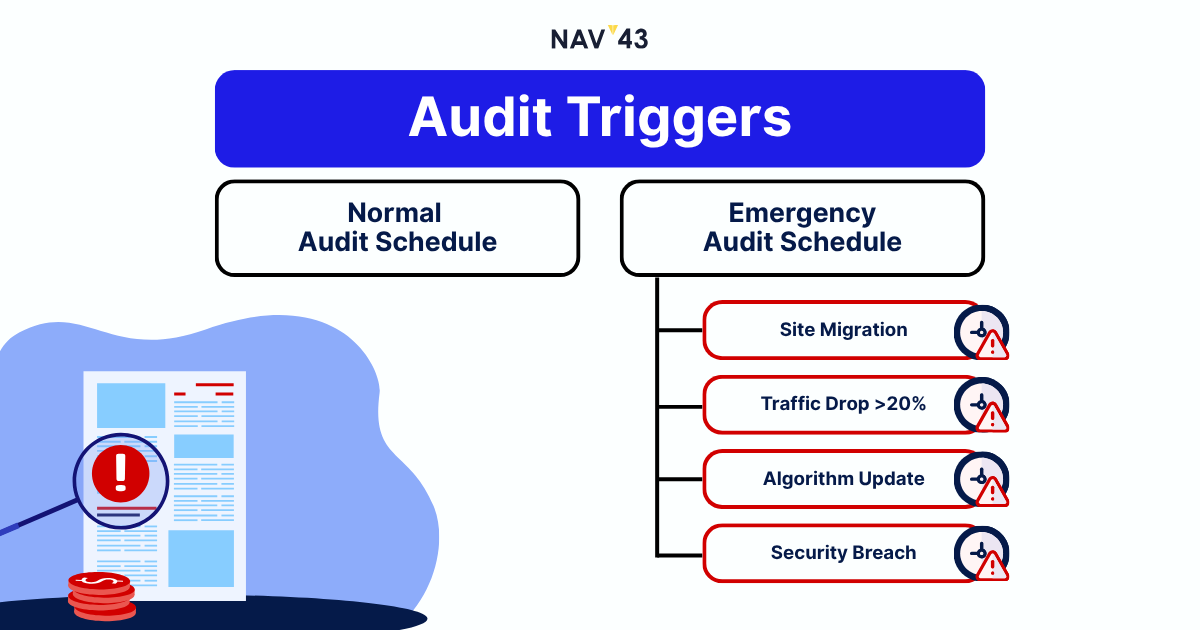
Sometimes waiting for your scheduled audit is like ignoring a check engine light. Certain events demand immediate SEO investigation, regardless of your regular cadence.
Site Relaunch or Migration
This is SEO’s highest-risk moment. I’ve seen migrations tank 60% of organic traffic overnight from seemingly minor oversights. Run three audits for any migration:
- Pre-migration audit: Document current state, identify must-preserve elements
- Staging audit: Catch issues before they go live
- Post-launch audit: Verify redirects, indexation, Core Web Vitals
After migration, submit an updated XML sitemap to Google Search Console to help search engine crawlers index the new site structure efficiently. Also, review and configure your robots.txt file to control the behavior of search engine crawlers during and after migration.
Common migration disasters include redirect chains, accidentally noindexed pages, canonical confusion, and internal linking breaks. A proper migration audit protocol prevents these expensive mistakes.
Core Algorithm Update Impact
When Google announces a core update, don’t panic, audit. Wait 2-3 weeks for rankings to stabilize, then run a focused audit examining:
- Content quality signals (E-E-A-T alignment)
- User experience metrics
- Technical health indicators
- Competitive landscape shifts
After major updates, review your structured data to ensure schema markup and rich snippets are still valid and correctly implemented.
The goal isn’t chasing the algorithm but understanding whether the update exposed existing weaknesses.
Sudden Traffic or Ranking Drops
A 20%+ organic traffic drop demands immediate investigation. Quick audit priorities:
- Search Console messages: Manual actions, security issues
- Indexation status: Pages suddenly deindexed?
- Crawl errors: Server issues blocking Googlebot?
- Competitive changes: New SERP features or competitors?
Speed matters here. Every day of declined traffic is lost revenue.
Security Breaches or Penalties
Security compromises require immediate SEO triage. Hackers often inject spammy content, create malicious redirects, or alter your robots.txt. Post-breach audit essentials:
- Full crawl for suspicious pages
- Outbound link audit for injected spam, including a review of external links
- Search Console security report review
- Disavow file preparation if needed
Large Content Operations
Launching 100+ pages? Deleting outdated content sections? These operations often create unintended SEO consequences. A post-launch audit catches:
- Orphaned pages from poor internal linking
- Cannibalization from similar content
- Crawl budget waste from low-quality pages
- Redirect requirement gaps
Also, review structured data to ensure schema markup and rich snippets remain accurate after large-scale changes.
Building a Repeatable Audit Calendar
Random audits produce random results. You need a systematic approach that integrates with your broader business calendar.
Setting Audit Goals and KPIs
Generic “improve SEO” goals waste everyone’s time. Define specific objectives for each audit cycle:
- Q1 Focus: Technical health post-holiday traffic surge
- Q2 Focus: Content optimization for peak season prep
- Q3 Focus: Mobile experience and Core Web Vitals
- Q4 Focus: Conversion optimization and site speed
Alongside technical audits, schedule a regular content audit to evaluate and improve website content performance.
Tie each audit to measurable KPIs: organic traffic growth, ranking improvements for target keywords, technical error reduction rates, Core Web Vitals scores.
Team Roles and Responsibilities
SEO audits fail when they’re one person’s side project. Assign clear roles:
- SEO Lead: Runs audit, prioritizes findings, creates action plan
- Developer: Reviews technical findings, estimates implementation effort
- Content Team: Handles on-page optimization, content gaps, reviews keyword usage and the page’s title for optimization
- UX/Design: Addresses user experience issues affecting SEO
- Project Manager: Ensures implementation happens on schedule
Calendar Integration Tips
Sync audit timing with your business rhythm:
- Schedule audits 2-3 weeks before quarterly planning
- Avoid audits during critical business periods (Black Friday, product launches)
- Build 4-6 week implementation windows post-audit
- Set calendar reminders for pre-audit data gathering
Documentation Best Practices
Your audit is only as good as its documentation. Create versioned audit reports showing:
- Issues found with severity ratings
- Recommendations with implementation priority
- Progress tracking from previous audits
- Resource requirements and timelines
Track improvements in search results visibility as a key outcome of your audits.
Store these in a central location accessible to all stakeholders. Version control prevents confusion when multiple team members reference findings.
Tools & Templates for Efficient Audits
The right toolkit transforms audits from overwhelming to systematic. Here’s what actually works in practice.
Essential Crawling Tools
Screaming Frog remains the workhorse for technical audits. Key configurations for efficient audits:
- Custom extraction for specific data points
- API integrations with Analytics and Search Console
- Scheduled crawls for automatic monitoring
- Check xml sitemaps for completeness and accuracy to ensure search engines can effectively crawl and index your site.
Sitebulb offers superior visualization for explaining issues to non-technical stakeholders. The crawl maps alone justify its cost when presenting to executives.
All-in-One Audit Platforms
Semrush Site Audit excels at ongoing monitoring. Set up weekly crawls for your most critical pages, monthly for the full site. The historical data helps identify when issues first appeared.
Ahrefs Site Audit integrates seamlessly with their backlink data. Particularly useful for identifying pages with strong backlinks but poor technical health, high-ROI optimization targets.
Performance Testing Arsenal
PageSpeed Insights provides Google’s perspective but test beyond it. Page speed is a critical metric to test and optimize for both user experience and search rankings. WebPageTest offers deeper performance insights with multiple test locations and connection speeds. For JavaScript-heavy sites, add Chrome DevTools performance profiling to your audit routine.
Reporting Templates That Drive Action
Skip 100-page PDF reports nobody reads. Build Looker Studio dashboards showing:
- Technical health score trends
- Priority issue tracking
- Implementation progress
- Business impact metrics
Addressing technical issues identified in your audit can significantly enhance user experience by improving website speed, security, and usability.
Templates should separate “FYI” data from “act now” findings. Executive summaries get two pages maximum with clear next steps.
For initial diagnostics, consider starting with a free seo audit using available online tools to quickly identify key issues and opportunities.
The Cost of Audit Procrastination
Delaying audits doesn’t save money, it defers costs while amplifying them. Unresolved technical issues from delayed audits can result in poor user experience, such as slow loading times or navigation errors, which further hurt your bottom line. Real examples from delayed audits:
- Migration disaster: $180K in lost revenue during 3-month recovery
- Indexation meltdown: 6 weeks of 50% traffic loss = $95K impact
- Core Web Vitals neglect: 28% conversion rate drop over 8 months
Compare those losses to audit costs (typically $5-15K quarterly for mid-size sites) and the ROI becomes obvious.
Attribution Models That Connect Audits to Revenue
Stop treating SEO audits as cost centers. Build attribution models showing:
- Organic traffic value (sessions × average session value)
- Ranking improvement revenue (position changes × click-through rate × conversion rate)
- Technical fix prevention value (potential downtime costs avoided)
- Competitive advantage value (market share protected/gained in the fast-paced online world)
When you present audits as revenue protection and growth investments rather than technical exercises, budget approval becomes straightforward.
Post-Audit Implementation
Completing an SEO audit is only half the battle, the real impact comes from implementing the recommended changes. Start by prioritizing critical technical SEO issues, such as fixing broken links, improving site speed, and resolving any crawl errors. Next, optimize on-page elements like title tags and meta descriptions to ensure every page is fully aligned with SEO best practices.
Create a detailed action plan that assigns responsibilities, sets deadlines, and tracks progress on each task. Ongoing SEO audits and regular monitoring are essential to maintain your website’s health and adapt to the latest search engine algorithms. By staying proactive and integrating SEO improvements into your digital marketing strategy, you’ll drive more organic traffic, enhance your online presence, and achieve your business goals in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Next Steps: Get Your Free Mini-Audit
Reading about audit frequency is step one. Knowing your site’s current health is step two. We’ve covered the what and when, now it’s time for action.
Ready to see where you stand? Request your free 50-point technical mini-audit and receive a personalized scorecard within 48 hours. We’ll analyze your site’s critical SEO vital signs and tell you straight: are you due for a comprehensive audit, or is your technical health solid? For long-term SEO health, it’s essential to schedule comprehensive SEO audits every three to six months or after major website changes to maintain search engine visibility and address technical issues.
-
Mini-audits work as spot checks between comprehensive reviews. They typically cover critical issues—indexation, major crawl errors, Core Web Vitals—in 2-3 hours. Think of them as SEO vital signs monitoring. For small sites, quarterly mini-audits supplemented by an annual deep dive provide solid coverage without overwhelming resources.
-
Comprehensive audits require 20-40 hours depending on site size and complexity. The timeline breaks down to: crawling and data gathering (4-8 hours), analysis and prioritization (8-16 hours), report creation and recommendations (8-16 hours). Rushing this process leads to missed issues and generic recommendations.
-
Automation handles data gathering efficiently, but interpretation requires human expertise. Set up automated crawls and monitoring, but plan manual review for strategy, prioritization, and business context. The best approach combines automated detection with strategic human analysis.
-
Technical audits focus on crawlability, indexation, site speed, and infrastructure. Content audits evaluate quality, relevance, optimization, and user value. While often performed separately, the most effective approach integrates both—technical issues impact content performance and vice versa.
-
Startups often need more frequent audits due to rapid changes and limited SEO maturity. Quarterly audits help establish good technical habits early. However, startups should focus on implementation over analysis—better to fix issues from quarterly audits than generate monthly reports nobody acts on.

