
Top 10 Common Technical SEO Mistakes to Avoid (and How to Fix Them) – 2025 Guide
Why Your Rankings Sink Despite Great Content

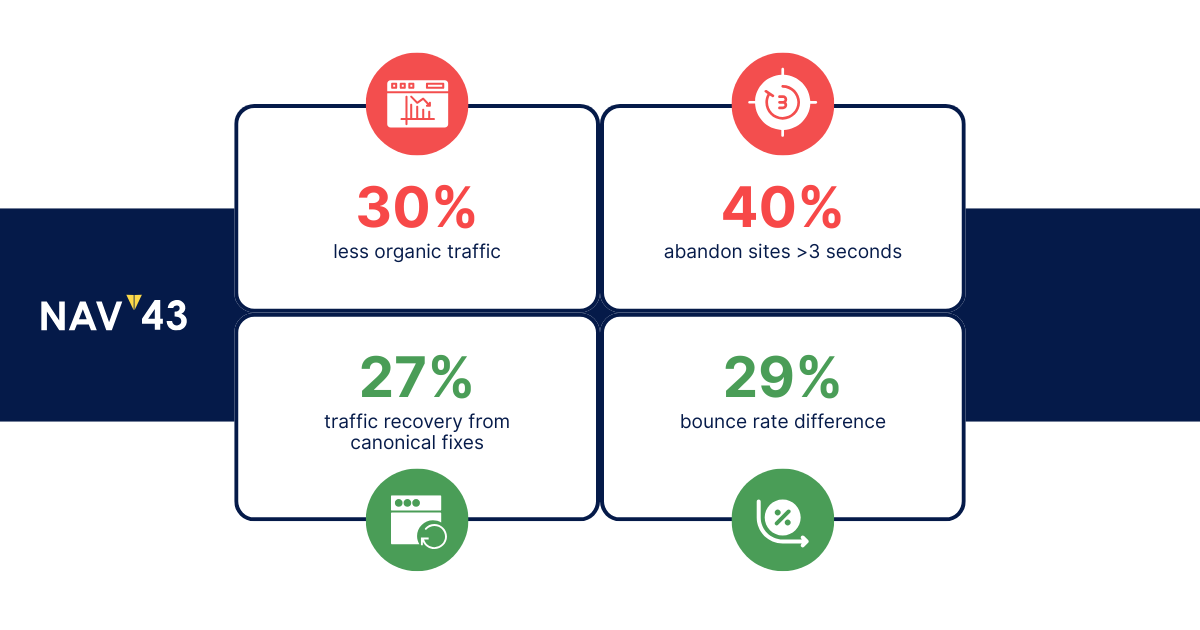
Your content might be exceptional, but if your site’s technical foundation is broken, you’re fighting a losing battle. The numbers don’t lie: sites with serious technical SEO issues experience up to 30% less organic traffic than their well-optimized counterparts. Even more alarming, 40% of users abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load.
I’ve audited hundreds of websites at NAV43, and the pattern is always the same. Businesses invest thousands in content creation while unknowable search engine crawl issues silently sabotage their efforts. These hidden problems compound over time, creating a cascade of SEO traffic loss that’s often attributed to algorithm updates or increased competition when the real culprit sits in the code.
The disconnect between content quality and search performance frustrates marketers and business owners alike. You publish regularly, optimize for target keywords (after thorough keyword research), build links, and focus on on page SEO and page SEO for individual web pages, yet traffic plateaus or declines. What’s missing? A solid technical foundation that allows search engines to properly crawl, index, and rank your content.
This guide exposes the 10 most damaging technical SEO mistakes I encounter during professional audits. Each section provides clear explanations of why these issues hurt your rankings, plus actionable fixes you can implement immediately. Whether you’re losing traffic to redirect chains, orphan pages, or Core Web Vitals failures, you’ll find practical solutions backed by real data.
At the end, I’ll share our comprehensive 120-point Technical SEO Audit Checklist, the same framework our team uses to diagnose and fix client sites. This resource has helped businesses recover lost rankings and unlock traffic they didn’t know they were missing. Addressing these technical SEO mistakes is essential, as they can seriously undermine your search engine optimization efforts.
1. Missing or Misconfigured Canonical Tags

Duplicate content remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of technical SEO. Without proper canonical tag SEO implementation, search engines struggle to determine which version of your content deserves to rank. Having the same content across multiple URL versions or the same page can cause issues, as search engines may not know which to prioritize. The result? Your PageRank gets diluted across multiple URLs, and none of them achieve their ranking potential.
Consider a typical e-commerce site. Product pages often generate dozens of duplicate URLs through filtering options, sorting parameters, and tracking codes. A single product might be accessible through:
- /product/blue-widget
- /product/blue-widget?color=blue
- /product/blue-widget?sort=price
- /product/blue-widget?utm_source=email
Multiple URL versions and indexing multiple URL versions can lead to duplicate content problems, making it harder for search engines to determine the preferred version.
Without canonicalization, Google treats each variation as a separate page competing for the same keywords. Studies show this duplicate content fix alone can recover up to 27% of lost organic traffic. The impact compounds when you factor in wasted crawl budget and confused ranking signals.
The solution requires strategic implementation of rel=canonical best practices. First, identify all URL variations using a crawler like Screaming Frog or Semrush. Then, choose your preferred URL structure and implement canonical tags pointing to it. Canonical tags tell search engines which version to index. For dynamic parameters and dynamically rendered pages, consider using Google’s URL parameter handling tool in Search Console to manage duplicate content generated by dynamic URLs.
Here’s the proper implementation:
< link rel=”canonical” href=”https://yoursite.com/product/blue-widget“ />
Place this in the head section of all duplicate pages. For sites migrating from HTTP to HTTPS or changing domain structures, combine canonicals with 301 redirects for maximum effectiveness. Remember, canonical tags are suggestions, while redirects are directives, use both strategically. For e-commerce sites, category pages are a common source of duplicate content and should also be properly canonicalized.
Duplicate content can negatively impact your title tags, page titles, and meta tags, leading to issues like duplicate or missing tags and reducing your visibility in search results.
Quick Fix Checklist
Audit duplicate URLs using crawling software. Set canonical tags on all variations. Implement 301 redirects for permanent URL changes. Validate implementation in Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool. Monitor organic traffic recovery over 30-60 days.
2. Orphan Pages (Unlinked Content)
Orphan pages represent a massive missed opportunity in most site architecture audits. These pages exist on your server but have zero internal links pointing to them, making them invisible to both users and search engine crawlers. Without an internal linking strategy, even your best content might never see the light of day.
The problem intensifies with larger sites. During a recent audit, we discovered a client had over 300 orphan pages, including several high-value service pages they wondered why weren’t ranking. These pages had strong content and even some external backlinks, but without internal links, they received no PageRank flow from the rest of the site.
Orphan pages SEO issues stem from various sources: old pages removed from navigation, content published without proper linking, or pages created for campaigns then forgotten. Whatever the cause, the solution remains consistent: systematic identification and strategic linking. When addressing orphan pages, it’s crucial to link them to other pages within your site to improve crawlability and prevent them from becoming isolated. Use relevant links and descriptive anchor text when adding internal links to ensure both users and search engines understand the context and value of the linked content.
Start by comparing your XML sitemap against a full site crawl. Pages appearing in the sitemap but not the crawl are likely orphans. Tools like Screaming Frog’s “List Mode” can crawl sitemap URLs directly, highlighting disconnected content. Once identified, evaluate each orphan page’s value. High-quality pages deserve contextual links from related content, especially content that addresses specific search queries. Low-value pages might need consolidation or removal.
The linking strategy matters as much as the discovery process. Don’t just dump orphan links in the footer. Instead, find relevant pages where these links add value. A orphaned case study belongs linked from your services page. An orphaned blog post fits naturally in related articles. This approach resurrects dead content while improving overall site structure.
Quick Fix Checklist
Crawl site and compare against XML sitemap. Identify valuable orphan pages worth saving. Add contextual internal links from relevant pages. Update navigation for important orphaned sections. Remove or redirect truly obsolete content.
3. Excessive Redirect Chains or Loops
Redirect chains represent one of the most common yet overlooked issues in redirect audit tools reports. Each additional hop in a redirect chain compounds problems: increased load time, diluted link equity, and wasted crawl budget. Google typically follows up to 5 redirects before giving up, but the damage starts with the second hop. If redirect chains are not managed properly, they can result in broken pages such as 4XX or 5XX errors, which negatively impact SEO and user experience. It’s also important to monitor external links to ensure they do not lead to redirect chains or broken pages, as this helps maintain site credibility and preserves link equity.
The mathematics of redirect chains reveals their true impact. With each redirect, you lose approximately 15% of link equity. A three-hop chain (A→B→C→D) means the final page receives only about 61% of the original PageRank. For competitive keywords, this loss often represents the difference between page one and page two rankings.
Understanding 301 vs 302 redirects adds another layer of complexity. While 301s pass most link equity, 302s (temporary redirects) pass significantly less. We frequently find sites using 302s for permanent moves, unknowingly handicapping their SEO. Even worse, mixing redirect types in chains creates unpredictable outcomes.
The fix requires systematic mapping of all redirects. Export redirects from your .htaccess file, server configuration, or CMS redirect manager. Use tools like Screaming Frog’s redirect chains report to visualize paths. Then, update each chain to point directly to the final destination. A chain like oldpage→category→subcategory→product should become oldpage→product.
Redirect chain SEO improvements often yield immediate results. One client reduced average page load time by 0.8 seconds simply by eliminating redirect chains. Their organic traffic increased 12% within six weeks as Google rewarded the improved user experience and crawl efficiency.
Quick Fix Checklist
Map all current redirect paths using crawling tools. Eliminate intermediate hops by pointing to final URLs. Convert 302s to 301s for permanent moves. Test updated redirects with HTTP status checkers. Monitor Core Web Vitals for speed improvements.
4. Non-Mobile-Friendly or Unresponsive Design
With mobile-first indexing now universal, a non-responsive site is essentially invisible to modern search. Google predominantly uses the mobile version of your content for indexing and ranking. If that mobile experience fails, your desktop rankings suffer too, regardless of how perfect the desktop version appears. Ignoring mobile optimization can significantly hinder your site’s success, as Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites and users expect seamless experiences on their devices.
The statistics paint a clear picture: nearly 60% of global web traffic comes from mobile devices. Yet many businesses still treat mobile as an afterthought. During audits, we regularly encounter sites with blocked resources on mobile, unplayable content, or layouts that require horizontal scrolling. Lacking a dedicated mobile site or failing to optimize mobile pages can result in poor user experience and lost rankings. These mobile usability errors directly translate to ranking penalties.
Responsive design SEO goes beyond simply fitting content on smaller screens. It requires rethinking user interactions, load priorities, and content hierarchy. Touch targets need adequate spacing. Forms must be finger-friendly. Images should scale appropriately without breaking layouts. Slow loading pages and slow page speed on mobile can negatively impact rankings, as users are quick to abandon sites that take too long to load.
The technical implementation starts with proper viewport configuration:
< meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1”>
But viewport tags alone don’t create responsive design. Your CSS must use flexible grids, fluid images, and media queries to adapt layouts. Modern frameworks like CSS Grid and Flexbox simplify this process, but many sites still rely on outdated fixed-width designs.
Testing reveals the truth. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test provides instant feedback on critical issues. Search Console’s Mobile Usability report tracks problems across your entire site. Pay special attention to text size, clickable element spacing, and content wider than screen errors. Each fix improves both rankings and user satisfaction.
Quick Fix Checklist
Implement responsive CSS with proper media queries. Add viewport meta tag to all pages. Test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Fix Mobile Usability errors in Search Console. Ensure feature parity between mobile and desktop versions.
5. Slow Page Load Times (Core Speed)
Speed kills, or in this case, slow speed kills conversions and rankings. The data is unforgiving: 83% of users expect pages to load within 3 seconds, and 40% abandon sites that take longer. For page speed optimization, every second counts. The difference between a 2-second and 5-second load time can mean a 29% difference in bounce rate.
Modern website performance audits must account for real-world conditions. Lab data from tools provides a starting point, but field data from actual users reveals the true picture. This is where Core Web Vitals speed metrics become crucial. Google uses real user data to assess page experience, making traditional optimization tactics insufficient. Broken images can significantly slow down page load times, negatively impacting both user experience and SEO. Detecting and fixing broken images during audits is essential for maintaining optimal site performance.
Image optimization remains the low-hanging fruit. During a recent audit, we found a client loading 15MB of images on their homepage, mostly uncompressed PNGs and oversized JPEGs. Simply converting to WebP format and implementing responsive images reduced page weight by 80%. The result? Their Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) dropped from 4.2 to 1.8 seconds. However, optimizing all page elements—including CSS files and layout stability (CLS)—is equally important for improving speed and ensuring a visually stable experience.
But images are just the beginning. JavaScript execution often represents the hidden performance killer. Third-party scripts for analytics, chat widgets, and social media can add seconds to load time. The solution isn’t removing these tools, it’s loading them intelligently. Defer non-critical scripts, lazy-load below-the-fold content, and consider facade patterns for embedded content.
Server response time forms the foundation of all speed metrics. If your server takes 2 seconds to respond, you’ve already failed Core Web Vitals before content even starts loading. Evaluate your hosting infrastructure, implement caching at multiple levels, and consider a CDN for global audiences. We’ve seen clients cut server response time by 70% simply by enabling proper caching headers.
Quick Fix Checklist
Compress and convert images to modern formats (WebP/AVIF). Minify CSS and JavaScript files. Implement lazy loading for below-fold content. Enable server-level caching and CDN. Defer non-critical third-party scripts.
6. Broken Internal Links (404 Errors)
Broken internal links create a double punishment: frustrated users and wasted PageRank. Every 404 error SEO impact compounds as link equity flows to a dead end instead of strengthening your site. What’s worse, these breaks often hide in plain sight, a revised URL here, a deleted page there, accumulating until they significantly damage your site’s performance. When broken links occur across multiple pages, the SEO issues are compounded, as duplicate content, duplicate meta tags, and keyword cannibalization can arise, further harming your search engine optimization efforts.
The mathematics of internal link maintenance reveals why this matters. Internal links distribute PageRank throughout your site, creating a hierarchy of importance. When links break, that flow stops. Pages downstream from broken links lose their share of authority, potentially dropping from rankings entirely.
During a recent audit, we discovered a major retailer had over 2,000 broken internal links following a site restructure. Product category pages linked to discontinued items. Blog posts referenced deleted resources. The navigation menu itself contained three broken links. The cumulative effect? A 23% drop in organic traffic over six months.
The process to fix broken links requires systematic detection and correction. Start with a comprehensive crawl to identify all 404s. But don’t stop there, also look for soft 404s, redirect chains ending in 404s, and links to redirected pages. Each represents an opportunity to reclaim lost link equity.
Fixing broken links isn’t just about updating URLs. Evaluate whether the target content should be restored, redirected, or removed entirely. For moved content, implement 301 redirects from the old URL. For truly deleted content, update the linking pages to remove or replace the broken links. This maintains user experience while preserving SEO value.
Quick Fix Checklist
Crawl site monthly to identify new 404 errors. Update internal links to point to current URLs. Implement 301 redirects for moved content. Remove links to permanently deleted pages. Monitor Search Console for crawl errors.
7. Improper robots.txt or Noindex Blocking
A single line in robots.txt can destroy your entire SEO strategy. Robots.txt mistakes often happen during development or staging, where developers block all crawling to prevent indexing of test content. The disaster occurs when these blocks migrate to production, effectively telling Google to ignore your entire site.
The danger of noindex tag SEO misuse extends beyond obvious blocks. We’ve seen sites accidentally noindex their blog categories, causing hundreds of posts to lose their primary path to discovery. Others have noindexed filtered product pages without implementing proper canonicals, creating orphaned content accessible only through direct links. Always check for the presence of the noindex meta tag on important pages, as incorrect use can prevent them from appearing in Google’s index and severely impact your search visibility.
Understanding crawl blocking issues requires distinguishing between robots.txt and noindex directives. Robots.txt prevents crawling, Google won’t even look at the page. Noindex allows crawling but prevents indexing, Google sees the page but won’t show it in results. Combining both creates confusion, as Google can’t crawl to see the noindex tag. It’s crucial to review all the pages on your site to ensure that only the intended ones are blocked or noindexed.
The horror stories are real. One client came to us after traffic dropped 95% overnight. The culprit? A developer added “Disallow: /“ to robots.txt during maintenance and forgot to remove it. Another client wondered why their new product pages weren’t ranking, they’d copied a template containing a noindex tag and applied it site-wide.
Prevention requires vigilance and proper testing protocols. Before any deployment, verify robots.txt allows crawling of important sections and double-check the website url in the robots.txt file for accuracy. Search your codebase for noindex tags. Use Google’s robots.txt tester to validate syntax. Most importantly, establish a post-deployment checklist that includes crawl verification.
Quick Fix Checklist
Audit robots.txt for overly broad disallow rules. Search templates and code for hidden noindex tags. Test robots.txt syntax with Google’s validator. Verify important pages allow crawling and indexing. Check Search Console coverage report for blocked resources.
8. Missing or Outdated XML Sitemap
Your XML sitemap SEO strategy directly impacts how quickly search engines discover and index new content. Yet many sites treat sitemaps as a one-time setup, creating them during launch and never updating them again. This neglect wastes opportunities for faster indexing and better crawl efficiency. For ecommerce sites, maintaining up-to-date xml sitemaps is especially important due to frequent product changes and large inventories, ensuring all relevant pages are indexed efficiently.
Modern sitemap best practices go beyond simply listing URLs. Your xml sitemaps should reflect your site’s current state, include only canonical URLs, and provide accurate last-modified dates. Including non-canonical URLs, redirects, or 404 pages sends mixed signals to search engines and wastes precious crawl budget.
The structure matters as much as the content. Large sites should implement sitemap indexes, breaking content into logical sub-sitemaps (products, categories, blog posts, etc.). This organization helps search engines understand your site structure and prioritize important sections. We’ve seen proper sitemap architecture reduce indexing time for new content from weeks to days.
Dynamic sitemap generation solves the staleness problem. Rather than manually updating sitemaps, implement systems that automatically reflect content changes. When you publish new content or update existing pages, your sitemap should update accordingly. This real-time accuracy helps Google discover changes faster.
Don’t forget to properly submit sitemap Google Search Console and reference it in robots.txt. The robots.txt reference ensures crawlers find your sitemap even if you haven’t submitted it through other channels. Monitor Search Console’s sitemap report for errors, tracking the ratio of submitted to indexed pages.
Quick Fix Checklist
Generate fresh sitemap including only canonical URLs. Remove redirects, 404s, and noindex pages. Add sitemap location to robots.txt file. Submit updated sitemap to Search Console. Implement automatic sitemap updates for content changes.
9. Mixed HTTP/HTTPS Content (SSL Issues)
Security warnings destroy user trust and rankings simultaneously. When browsers detect mixed content on HTTPS pages, they display warnings or block resources entirely. This creates broken functionality and poor user experience,exactly what Google’s algorithms penalize.
The transition to HTTPS SEO ranking benefits should be complete, not partial. Yet we regularly find sites serving pages over HTTPS while loading images, scripts, or stylesheets over HTTP. Modern browsers block this “active mixed content” by default, breaking functionality and creating visible errors that damage credibility.
The SSL certificate setup represents just the first step. After installing SSL, you must update every internal resource reference to use HTTPS. This includes images in content, CSS background images, JavaScript files, fonts, and even form action URLs. Missing even one creates mixed content warnings.
Hard-coded HTTP references hide throughout older sites. They lurk in database content, theme files, plugins, and custom code. A systematic approach to mixed content fix requires searching and replacing across all these locations. Database search-and-replace tools can update content, while code reviews catch template issues.
Implementation should include HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) headers, forcing browsers to use HTTPS exclusively. This prevents downgrade attacks and eliminates the possibility of accessing HTTP versions. Combined with proper redirects, HSTS ensures users always reach the secure version of your site.
Quick Fix Checklist
Force HTTPS redirects for all HTTP requests. Update all internal links and resources to HTTPS. Implement HSTS headers for strict security. Fix mixed content warnings in browser console. Monitor Search Console for security issues.
10. Poor Core Web Vitals / Page Experience
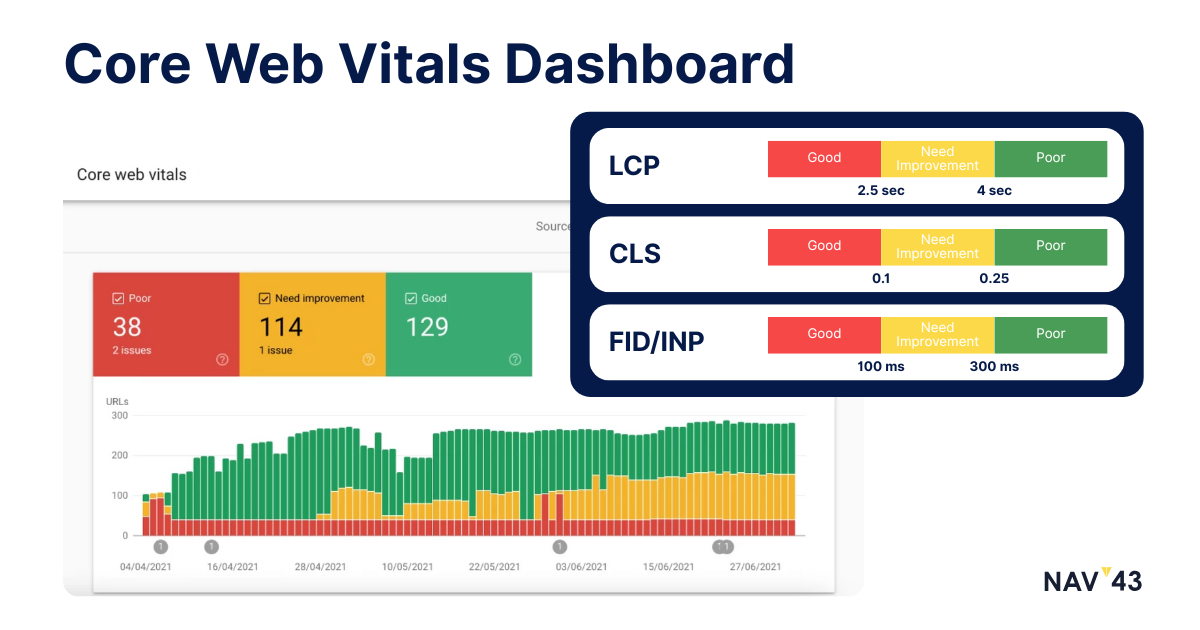
Core Web Vitals optimization represents Google’s clearest signal about ranking factors. These metrics,measuring loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability,directly impact rankings. Sites failing Core Web Vitals face an uphill battle for competitive keywords, regardless of content quality.
Understanding LCP FID CLS metrics requires thinking like a user. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures when the main content loads,users judge speed by when they see meaningful content, not when technical loading completes. First Input Delay (FID) or Interaction to Next Paint (INP) captures responsiveness,can users immediately interact, or does the page freeze? Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) quantifies visual stability,does content jump around as it loads?
The page experience update made these metrics ranking factors, but their importance extends beyond SEO. Poor Core Web Vitals correlate with higher bounce rates and lower conversions. Users don’t distinguish between slow servers and heavy JavaScript,they just leave.
Optimization requires addressing each metric individually. For LCP, optimize your largest above-fold element,usually a hero image or heading. Preload critical resources, optimize server response, and eliminate render-blocking resources. One client improved LCP from 4.1 to 1.9 seconds simply by preloading their hero image font.
FID/INP improvements focus on JavaScript efficiency. Break up long tasks, defer non-critical scripts, and implement code splitting. CLS fixes require reserving space for dynamic content. Set explicit dimensions for images and videos, load fonts intelligently, and avoid inserting content above existing elements. Optimizing page elements, such as CSS files and layout structure, is crucial for maintaining visual stability and reducing unexpected layout shifts.
Quick Fix Checklist
Test pages with PageSpeed Insights for Vitals scores. Optimize largest content element for better LCP. Reduce JavaScript execution for improved FID/INP. Set dimensions on all media to prevent CLS. Monitor field data in Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report.
Critical But Overlooked: Image Optimization for SEO
Image optimization is a cornerstone of technical SEO that many site owners underestimate. While high-quality visuals can enhance user experience, unoptimized images can quietly undermine your search engine rankings and overall search visibility. Large, uncompressed images slow down web page loading times, making it harder for search engines to efficiently crawl and index your content. This not only frustrates users but also signals to search engines that your site may not provide the best experience, which can negatively impact your search rankings.
Beyond speed, image optimization also plays a role in preventing duplicate content issues. When images are uploaded in multiple sizes or formats without proper management, search engines may index several versions of the same image. This can dilute the authority of your web page and confuse search engines about which version to prioritize, ultimately hurting your technical SEO efforts.
How Unoptimized Images Hurt Rankings
Unoptimized images can drag down your search rankings in several key ways. First, large image files increase page load times, and search engines like Google factor site speed heavily into their ranking algorithms. Slow-loading web pages lead to higher bounce rates and a poor user experience, both of which can push your site lower in search results.
Second, when multiple versions of the same image exist across your site, search engines may index each one separately. This creates duplicate content issues that can confuse search engines and dilute the ranking power of your web pages. Instead of consolidating authority to a single, relevant page, your site’s ranking signals are spread thin, making it harder to achieve top positions in search results.
Finally, if images lack descriptive file names, alt text, or structured data, search engines struggle to understand their context and relevance. This reduces the chances of your images appearing in image search results and can limit the overall visibility of your web pages. Optimizing images for both speed and context ensures that your site delivers a seamless user experience and maximizes its search engine rankings.
Is Your Website Structure Holding You Back?
A well-organized website structure is fundamental to both user experience and technical SEO success. When your site’s architecture is clear and logical, search engines can more easily crawl and index your web pages, leading to improved search rankings and greater search visibility. On the flip side, a disorganized or confusing site structure can create indexing challenges, duplicate content problems, and ultimately limit your site’s ability to perform well in search results.
Poor website structure often results in important pages being buried deep within the site, making them harder for both users and search engines to find. This can lead to missed opportunities for ranking high-value content and can even cause search engines to overlook key sections of your site entirely.
Why Site Architecture Matters for SEO
Site architecture is a critical component of SEO because it helps search engines understand the hierarchy and relationships between your web pages. A well-structured site, with clearly defined categories and subcategories, allows search engines to identify which pages are most important and how content is organized. This clarity not only improves your site’s chances of ranking for relevant search queries but also enhances the user experience by making navigation intuitive and efficient.
Internal linking is a powerful tool in this process. By strategically linking related pages, you guide both users and search engine crawlers through your site, ensuring that important pages receive the attention and authority they deserve. Proper use of canonical tags further helps prevent duplicate content issues by signaling to search engines which version of a page should be indexed.
Ultimately, a strong site architecture supports higher search engine rankings and better user engagement. By making it easy for search engines to crawl and understand your site, and for users to find what they need, you set the foundation for long-term SEO success.
Putting It All Together – Building a Bulletproof Technical SEO Roadmap
Creating a comprehensive technical SEO audit checklist transforms overwhelming problems into manageable tasks. The key lies in prioritization and systematic execution. Not all issues carry equal weight,a site-wide noindex disaster demands immediate attention, while optimizing image formats can wait.
Start your SEO roadmap by categorizing issues into three buckets: critical (blocking indexing or causing major UX problems), important (affecting performance but not catastrophic), and nice-to-have (optimizations that provide incremental benefits). This framework prevents paralysis and ensures you tackle high-impact problems first.
Successful ongoing site maintenance requires shifting from reactive to proactive management. Implement monthly technical audits to catch issues before they compound. Set up alerts in Search Console for coverage errors, security issues, and Core Web Vitals failures. Create documentation for common fixes so team members can address issues independently. For international and regional SEO strategies, it’s important to connect with local search engines and implement local SEO best practices, such as using hreflang tags and interlinking regional or language versions. Many ecommerce sites benefit from implementing structured data markup, as it helps search engines understand website content and can lead to enhanced rich snippets and improved visibility.
The compound effect of fixing multiple technical issues often surprises site owners. Individual fixes might seem minor, but combined improvements create dramatic results. We’ve seen sites double their organic traffic within six months simply by systematically addressing the issues outlined in this guide.
Remember that technical SEO isn’t a one-time project,it’s an ongoing commitment. Google’s requirements evolve, your site grows, and new issues emerge. Building technical excellence into your workflow ensures long-term success rather than periodic crisis management.
Download Your Free 120-Point Technical SEO Audit Checklist
Ready to find and fix every hidden issue on your site? Click below to download our proven 120-point Technical SEO Audit Checklist and start boosting your organic traffic today.
What You’ll Get With Our Technical SEO Audit Checklist
This isn’t another generic SEO checklist. Our 120-point audit framework comes directly from NAV43’s client work, refined through hundreds of successful technical audits. The editable Google Sheets format lets you customize it for your specific needs while maintaining a proven structure that catches issues others miss.
Each audit point includes priority labels (Critical, High, Medium, Low) so you know exactly where to focus first. We’ve added resource links for tools and documentation, saving hours of research. Step-by-step instructions guide you through complex checks, making advanced audits accessible even for SEO beginners.
The checklist covers every aspect discussed in this guide plus advanced topics like structured data markup, structured data validation, international SEO configuration, and JavaScript rendering issues. You’ll also receive our proprietary scoring system that quantifies technical health, helping you track improvements over time and demonstrate ROI.
Take Action Today
Spotted a technical issue but lack bandwidth? Book a free 30-minute consultation with our senior SEO specialists and get a custom action plan tailored to your site’s specific challenges and opportunities.

